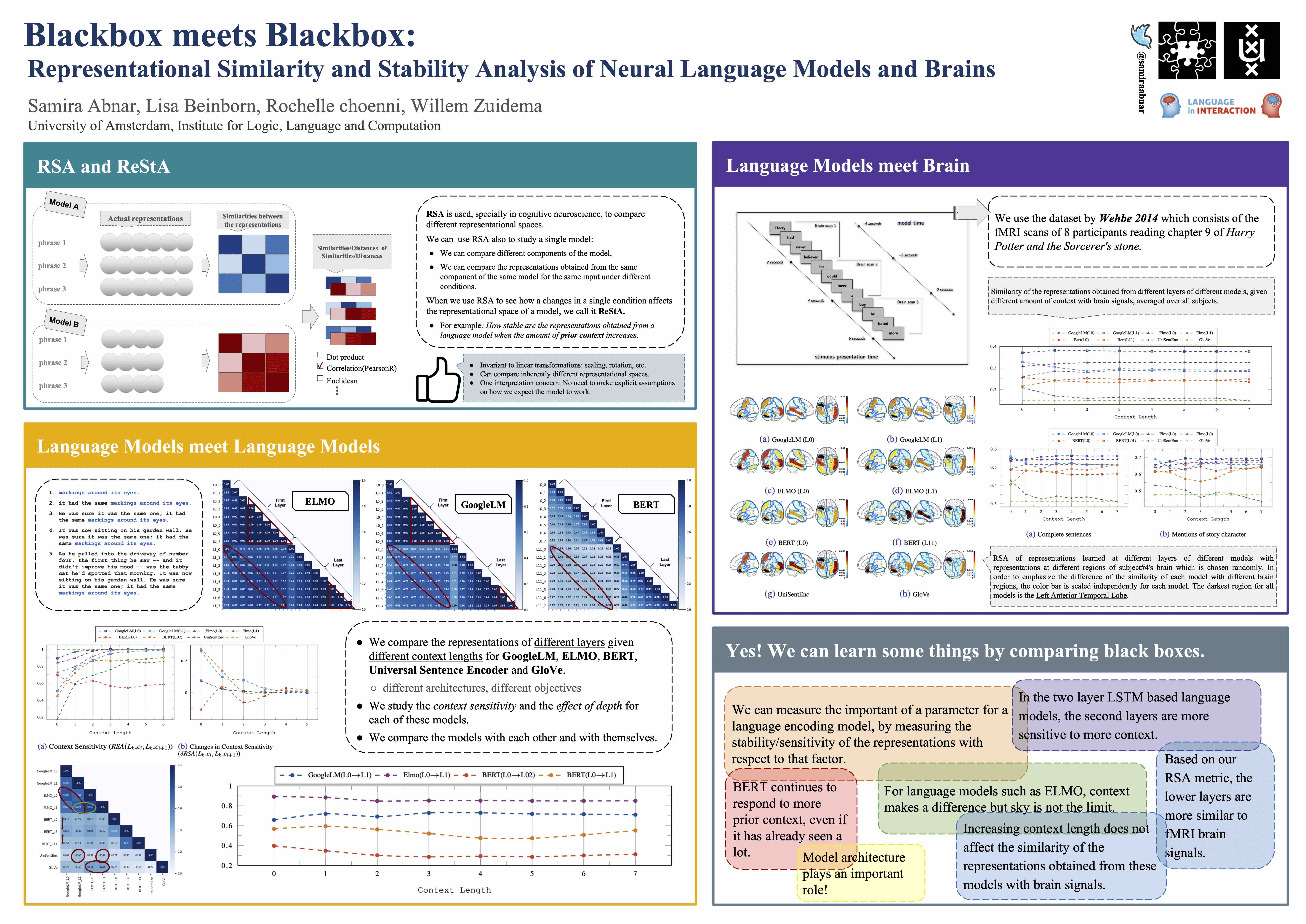
Distilling Inductive Biases
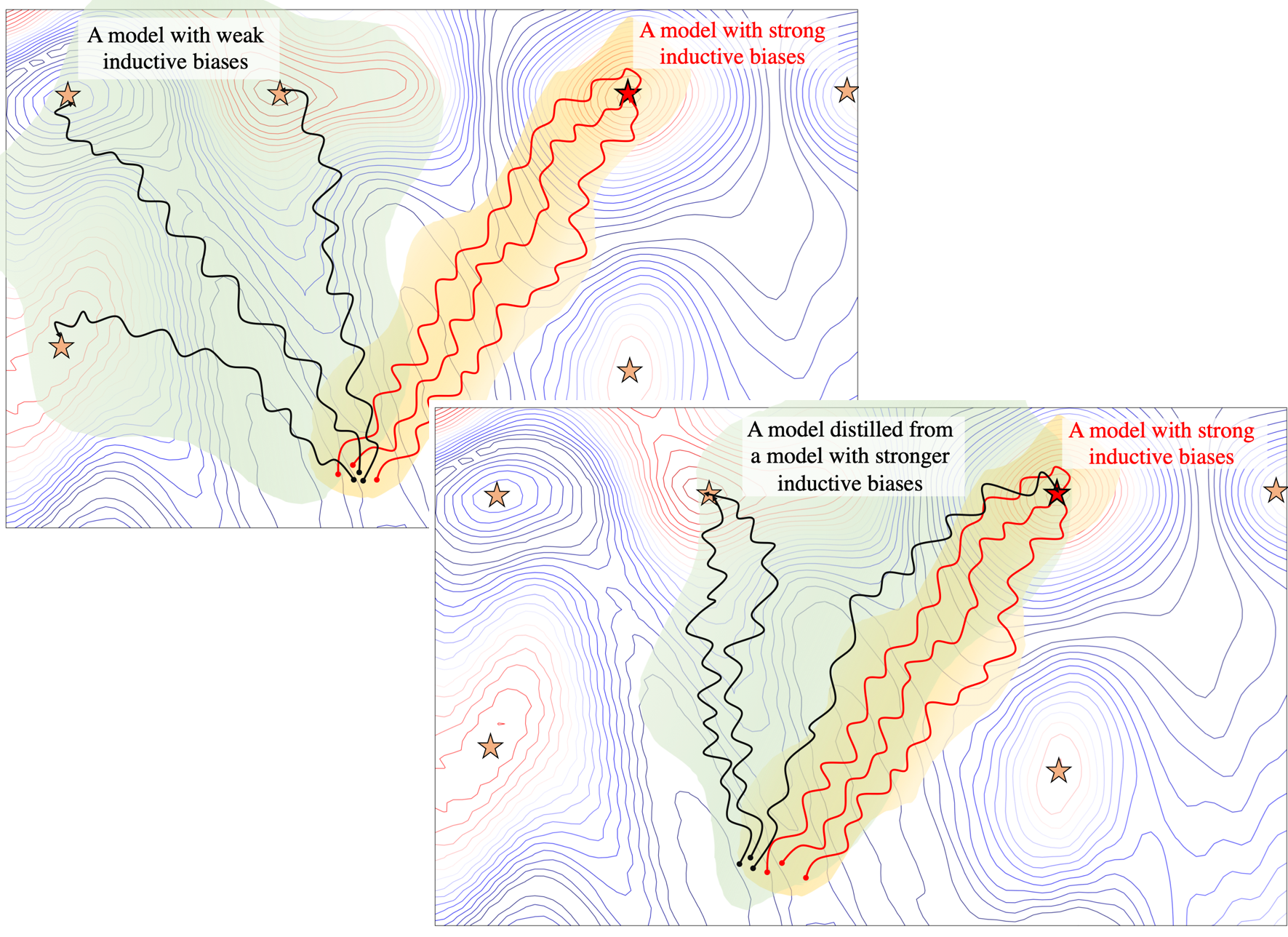
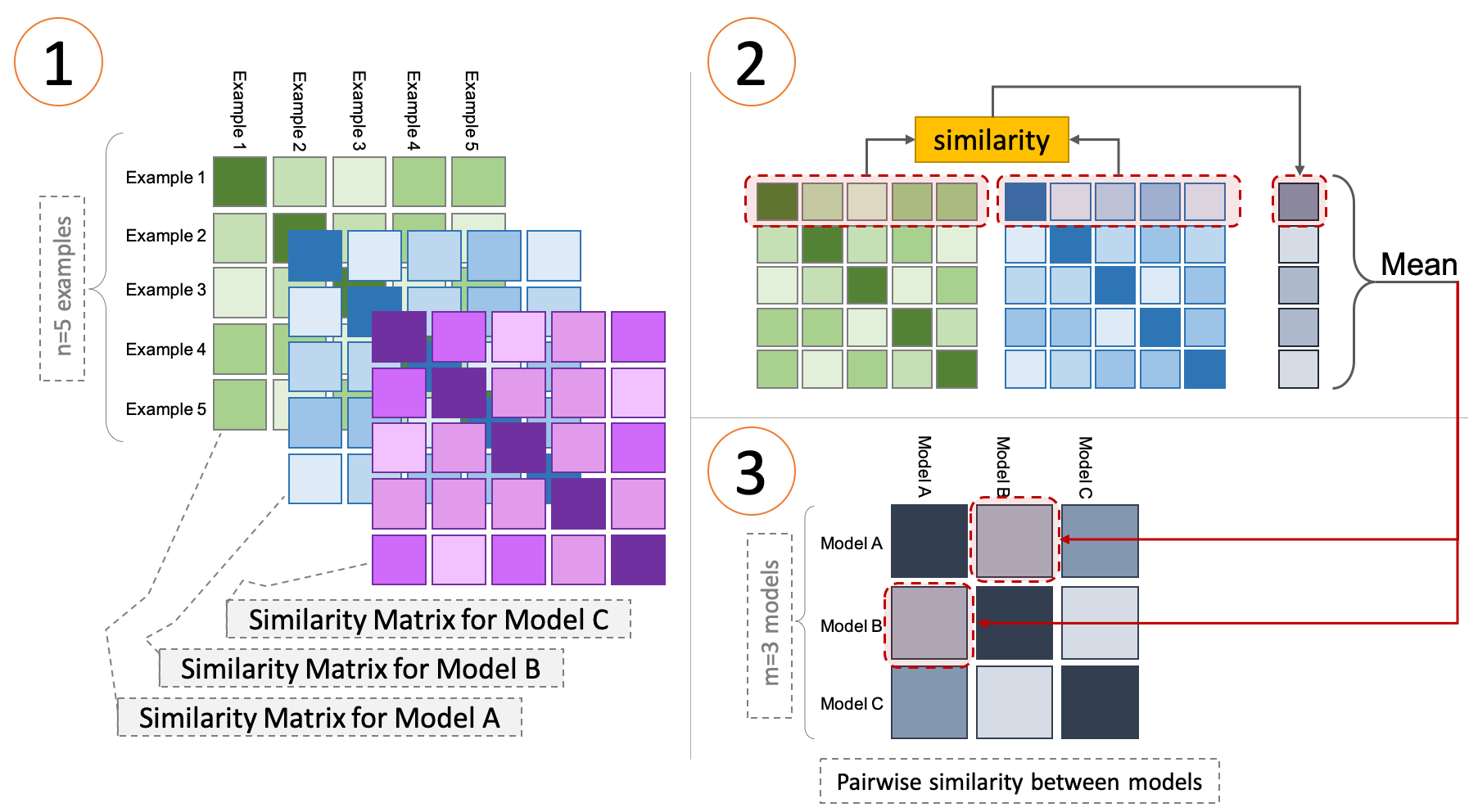
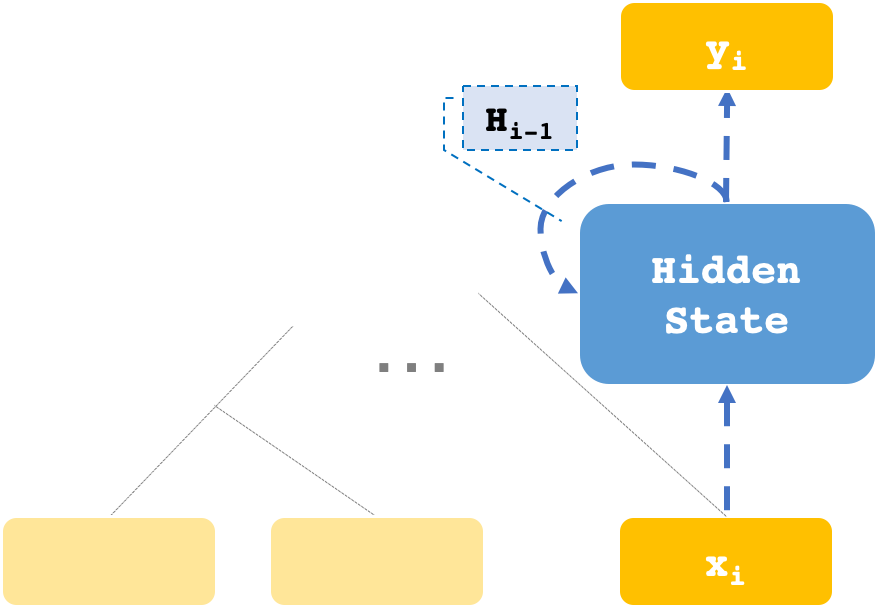
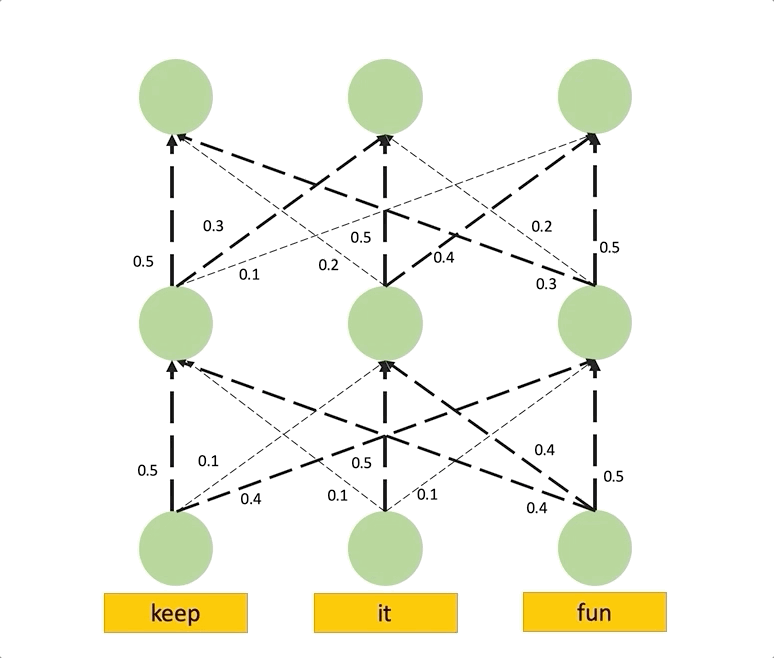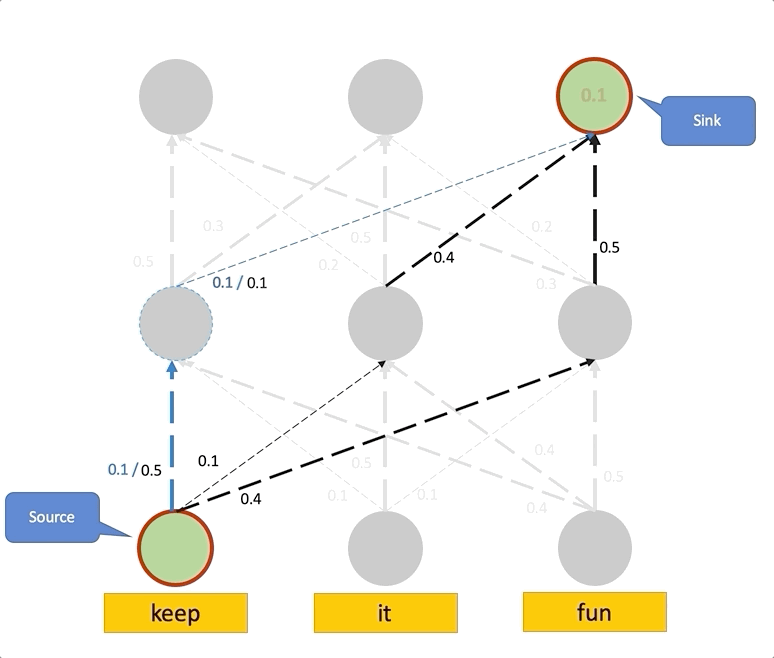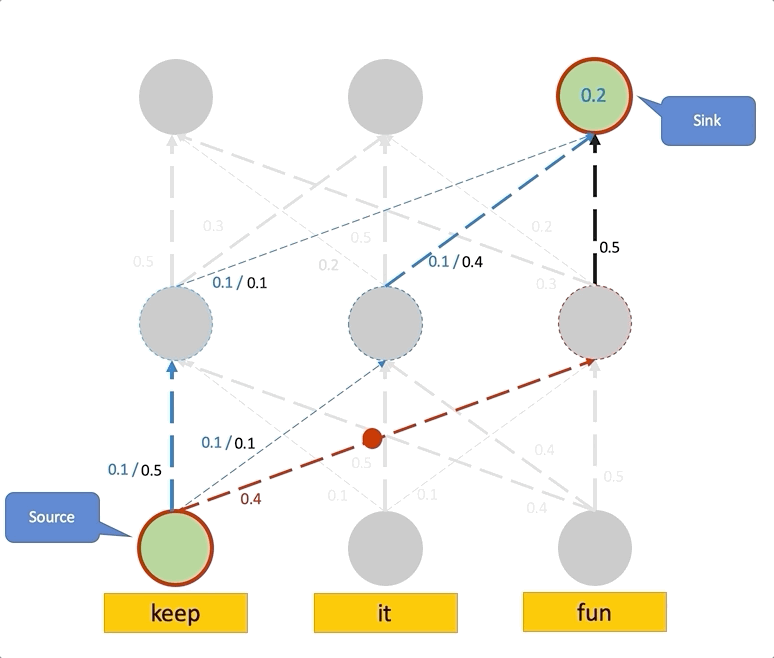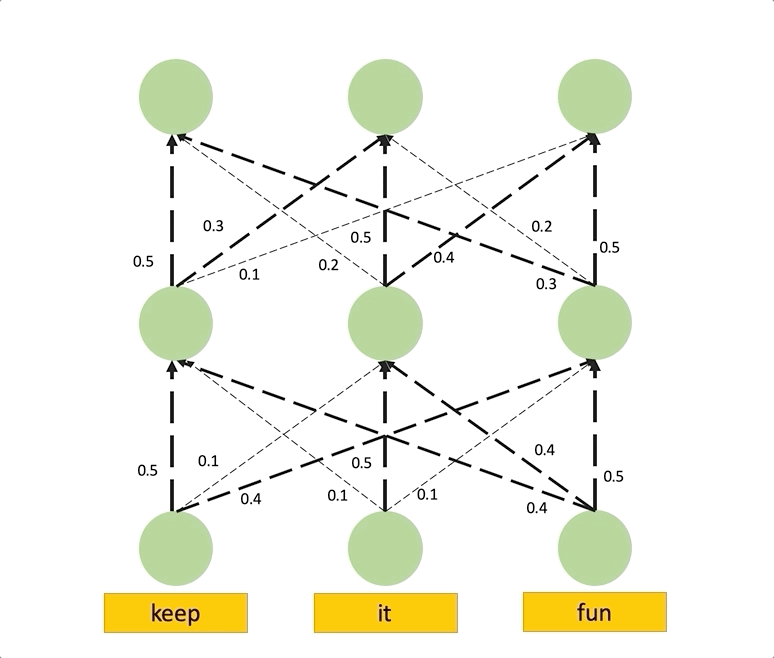
Having the right inductive biases can be crucial in many tasks or scenarios where data or computing resources are a limiting factor, or where training data is not perfectly representative of the conditions at test time. However, defining, designing and efficiently adapting inductive biases is not necessarily straightforward. In this post, I discuss our paper, "Transferring Inductive Biases Through Knowledge Distillation", where we explore the power of knowledge distillation for transferring the effect of inductive biases from one model to another.